
Several approaches have been applied to compensate such loss in quality, including the use of salt substitutes, combination of indigenous cultures, pretreatment of raw material and starter cultures encapsulation. Detailed Project Report (DPR) on fat powder and soya sauce powder Present Market Position and Expected Future Demand, Technology, Manufacturing Process, Investment Opportunity, Plant Economics and Project Financials. Although salt reduction can accelerate the microbial growth, the flavor quality of soy sauce is compromised. Attempts to enhance and accelerate flavor formation in the presence of high salt concentration include the inoculation with mixed starter cultures, genetic modification, cell, and enzyme immobilization.
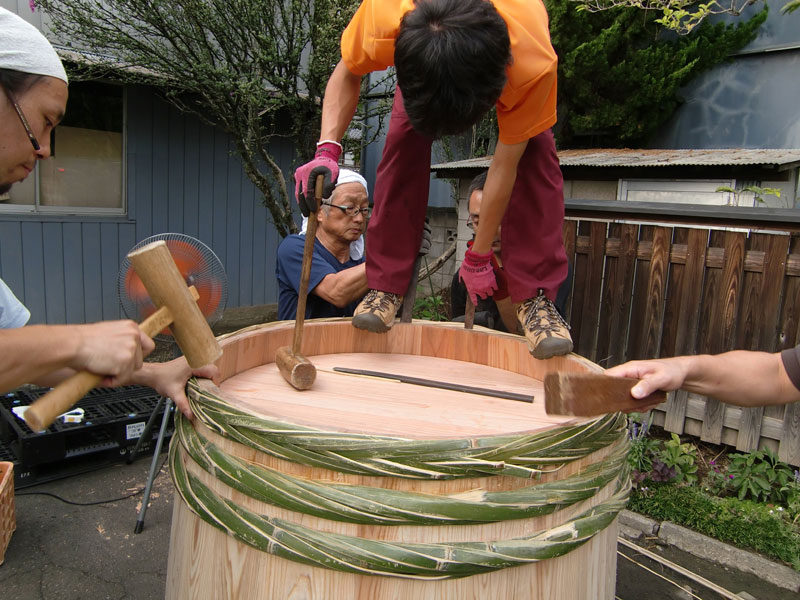

Furthermore, microbial interactions in moromi fermentation are affected by current efforts to reduce salt in soy sauce, in order to tackle slow fermentation due to low metabolic activity of microbes and increased health risk related to high sodium intake. Despite their importance for producing a wide range of volatile compounds, antagonism can occur due to different growth condition requirements. Tetragenococcus halophilus and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii are predominant among the microbes involved in the moromi stage. They are mixed and used for koji (malt) making. General Flow Chart of Kecap Manufacturing Process. Foods, an international, peer-reviewed Open Access journal. This might be due to the dierences of production process employed. those of the Japanese soy sauce, except one salty type kecap. Complex microbial interactions play an essential role in its flavor development during the fermentation. Soy Sauce Manufacturing Process (1) Cooking Ingredients Soybeans are steamed. Moreover, dierences of volatile compounds detected from both soy sauces were noted. Soy sauce is an increasingly popular oriental fermented condiment produced through a two-step fermentation process called koji (solid-state fermentation) and moromi (brine fermentation).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
